Germany’s parks plant a way forward on climate change
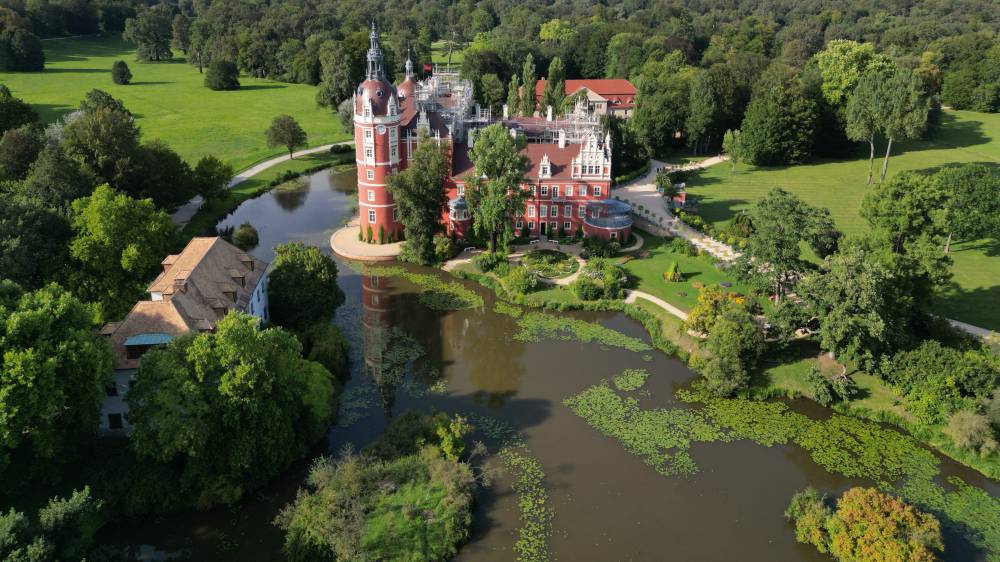

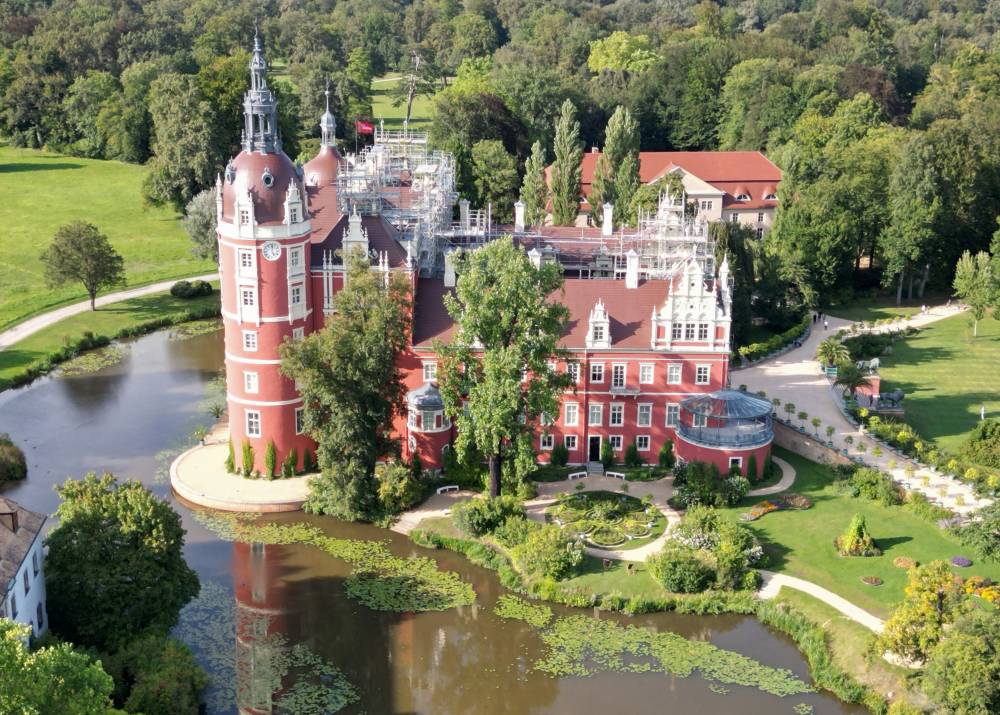
BAD MUSKAU, GERMANY—In the castle gardens of Muskauer Park, which straddles both banks of the German-Polish river border, caretakers have mounted a fightback against the impacts of climate change.
On the stump of a 150-year-old oak tree, gnawed by parasites and felled in a storm, a tender new shoot represents the estate’s hope of adapting to rising temperatures and more frequent droughts.
As part of a “natural regeneration” project, the sapling was grafted onto its fallen predecessor by gardeners in the first step towards replacing the UNESCO-listed park’s lost trees.
The young oak “will benefit from the roots of the old tree and will be more resistant to threats,” gardener Jana Kretschmer told AFP.
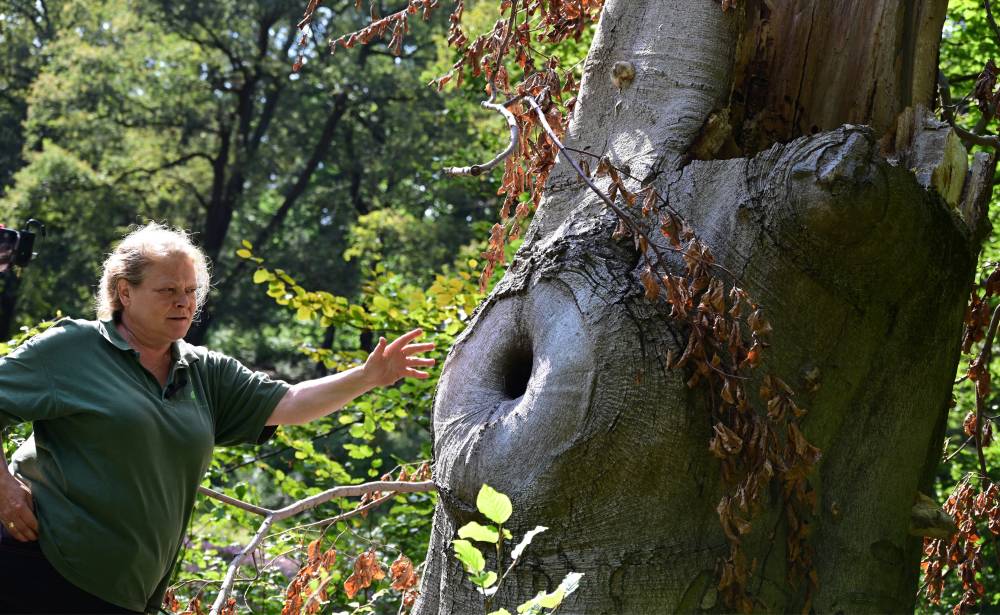

By transmitting their DNA to the new saplings, the older trees “teach” their descendants how to adapt to less hospitable conditions.
“Nature shows the way, humans need only look on,” said Kretschmer.
Drought and pests are among the silent killers encouraged by climate change, which weakens plants and has started to decimate the flora of the parklands on both sides of the Neisse river.
Some 180 beeches, ashes and oaks had to be felled there last year.
“Every year since 2018 we have to cut down more and more trees,” said Kretschmer, the site’s deputy manager, who bemoaned the loss of countless old trees as a “catastrophe.”

Natural cure
In June 15, German estates presented their plans to protect their gardens against the impacts of climate change.
At Muskauer Park, the groundskeepers are betting on the traditional method of natural regeneration to increase the tree-count.
Importing more resistant species of trees would be an option, but one that would be “neither sustainable, nor intelligent,” said park manager Cord Panning.
A natural regeneration approach moreover promises savings in two scarce commodities: money and water.
Following the method, caretakers select the best young specimens to plant them in place of old trees, eschewing genetic engineering or any foreign transplants.

In time, they hope to restore virtually all of the trees in the 19th century garden that have been lost and felled.
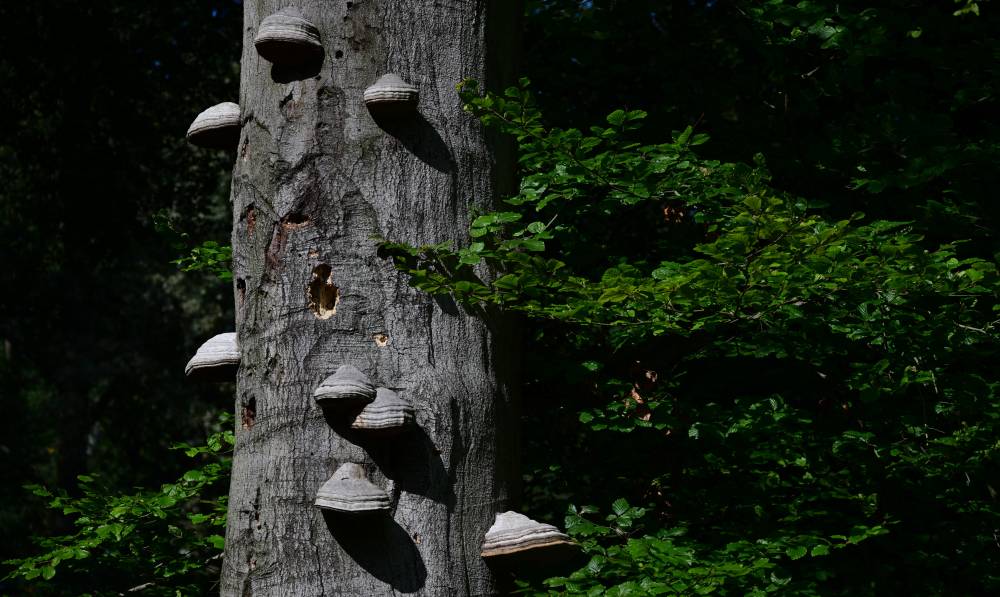
Among the pests to have plagued the trees at Muskauer Park are the tinder fungus and the bark beetle.
“Usually, by the time you realize it, it is too late,” said Kretschmer.
Long dry spells between 2018 and 2020 did nothing to help the situation, leaving the trees ever more vulnerable to attack.
Fungal invasion
Further south in Germany, at Nymphenburg Palace in Munich, the spread of the phytophthora fungus and invasive mistletoe species are depriving trees of water.
“The trees are experiencing dry stress, even in years where rainfall is sufficient,” said Michael Degle, the palace’s landscape architect.
The Munich park has had a system of “sustainable tree management” since 2018, which employs moisture sensors and new pruning techniques.

The project feeds into the joint efforts of over a dozen garden estates in Germany, including Muskauer Park, to develop effective responses to climate change.
But their work is “reaching its limits,” according to the group’s June report.
Already, 20 to 30 percent of their budget is spent on fixing climate damage—a share which is only increasing.
According to their calculations, somewhere between $220 and $275 million would be needed in the long term to protect historic parks from rising temperatures.
The damage to trees at Muskauer Park by a warming climate will be on show at the estate’s open day at the end of September.
An opportunity, according to Kretschmer, to show that trees “are not just wood, but living beings much more clever than us.”
AFP is one of the world's three major news agencies, and the only European one. Its mission is to provide rapid, comprehensive, impartial and verified coverage of the news and issues that shape our daily lives.