Japanese brewer hopes Unesco listing makes sake as popular as sushi
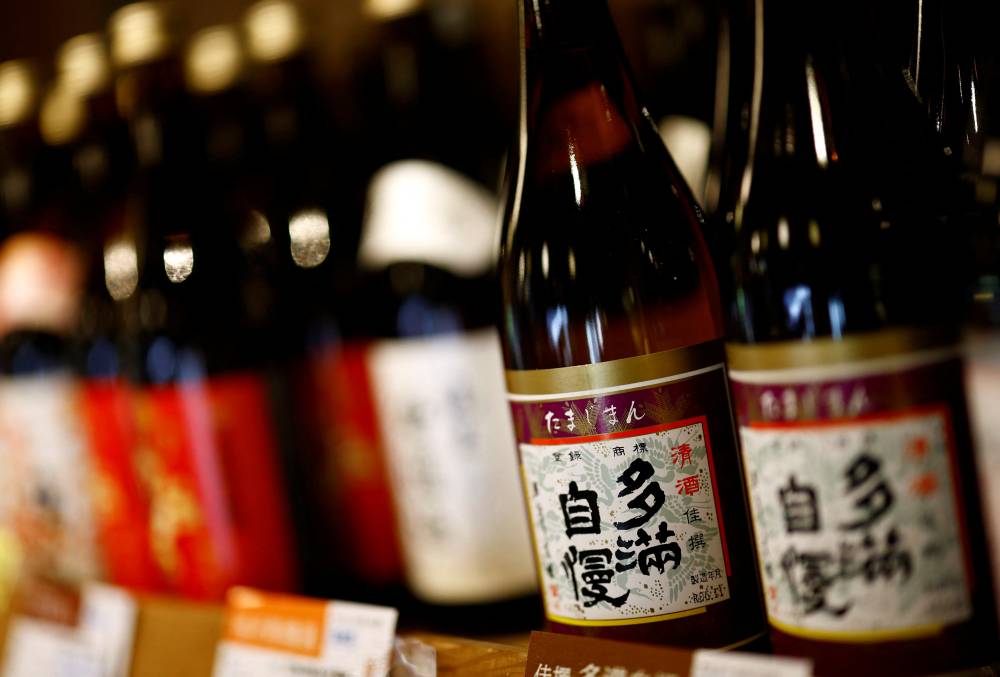

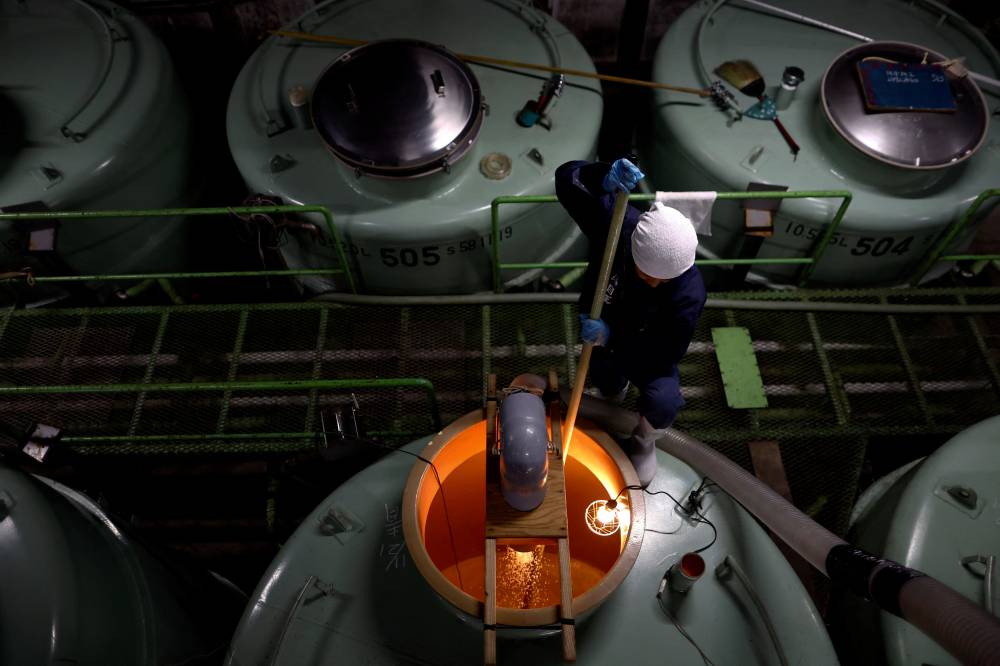
FUSSA, JAPAN—At a Tokyo brewery dating back to the days of the samurai, Koichi Maesako drops a 3-meter-long wooden paddle into a giant, jade-colored tank and gently stirs the white mixture that will turn into sake in a week’s time.
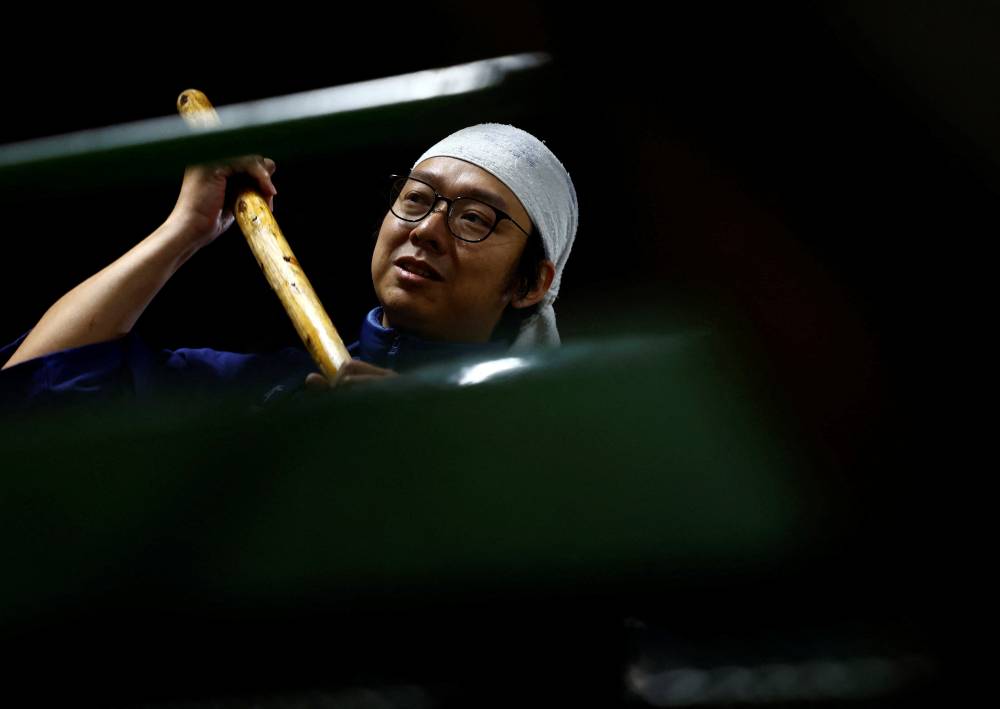

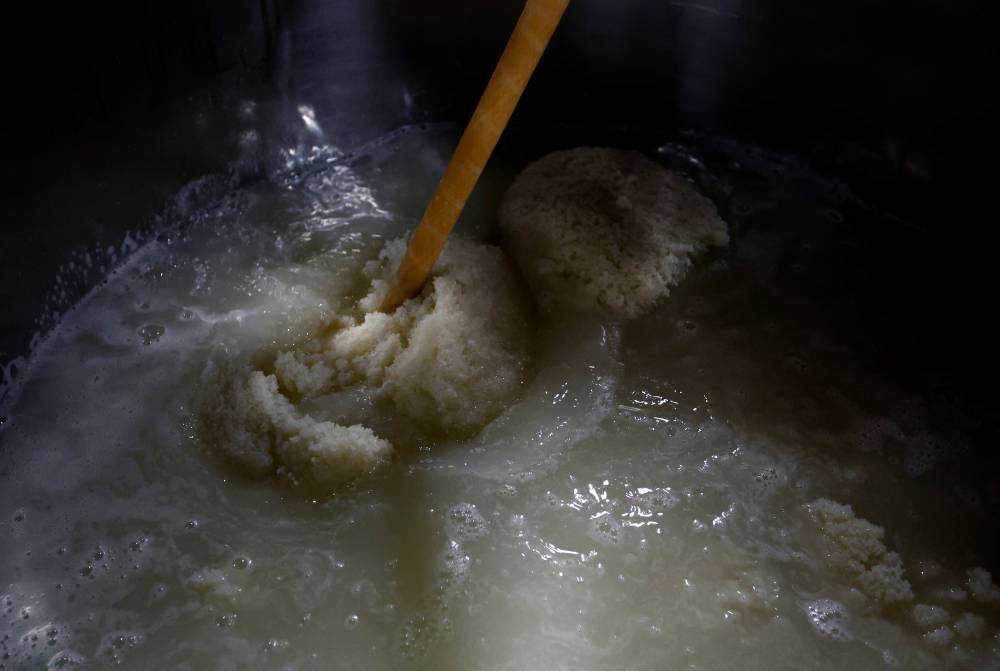
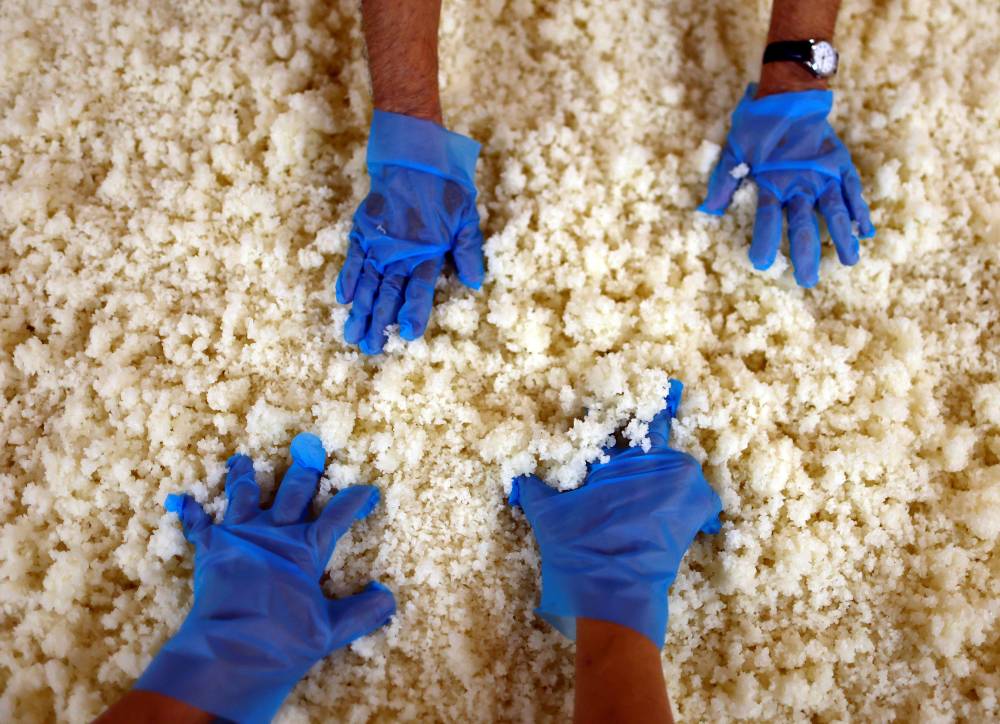
The sweet-and-sour-smelling brew—of rice, yeast starter, the culinary mold known as koji and water—has been fermenting for 20 days in what is part of an ancient technique that Unesco is set to list as Intangible Cultural Heritage this week.
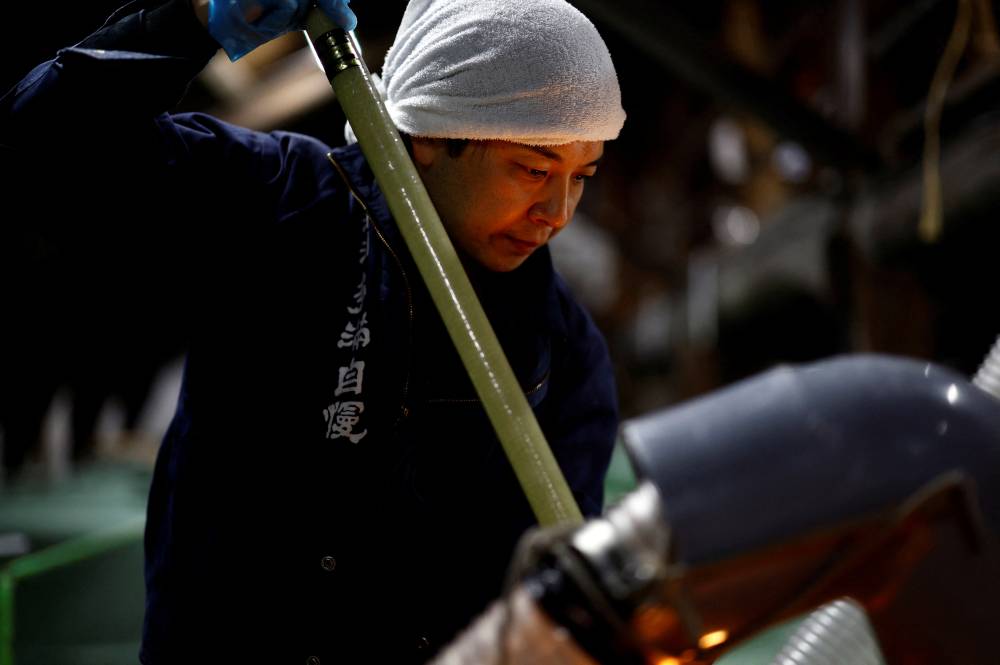
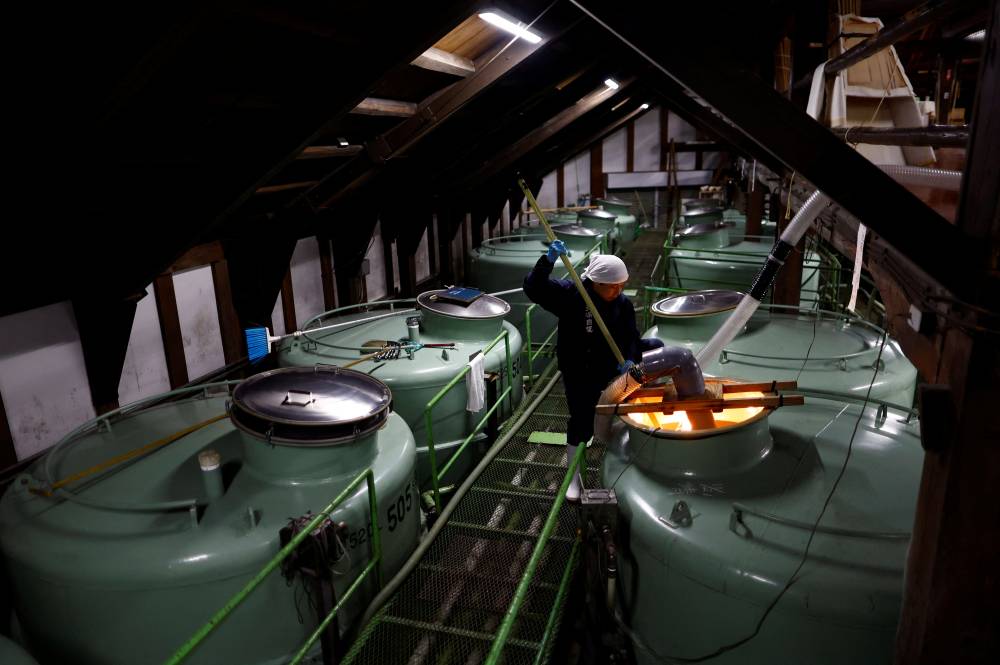


For Maesako, the 40-year-old chief brewer of Ishikawa Shuzou, or Ishikawa Brewery, the UN agency’s endorsement would be welcome news after a difficult couple of years.
Unseasonably warm weather has hit the rice harvest, not only affecting the quality of the grain but also raising procurement costs, he said.
Traditional sake brewers had already been contending with decades of falling sales at home as consumers acquired a taste for cocktails like highballs and other alcoholic drinks.

“The situation is much tougher compared to previous years,” Maesako told Reuters last week.
“It’s still quite warm, even though it’s almost December. The price of rice is high and the harvest is poor, which has made sake-brewing (this year) very challenging.”

Maesako hopes the UN body’s recognition of the traditional brewing technique will turn things around by igniting demand overseas, where sake has slowly gained popularity alongside Japanese cuisine, also in part thanks to Unesco’s endorsement of “washoku” as living heritage in 2013.
“After being listed by Unesco, Japanese traditional cuisine (washoku) has spread all over the world,” Maesako said.

“I hope that the same thing will happen with sake. Our brewery is seeing a rise in exports, and we hope the Unesco listing will accelerate this trend.”
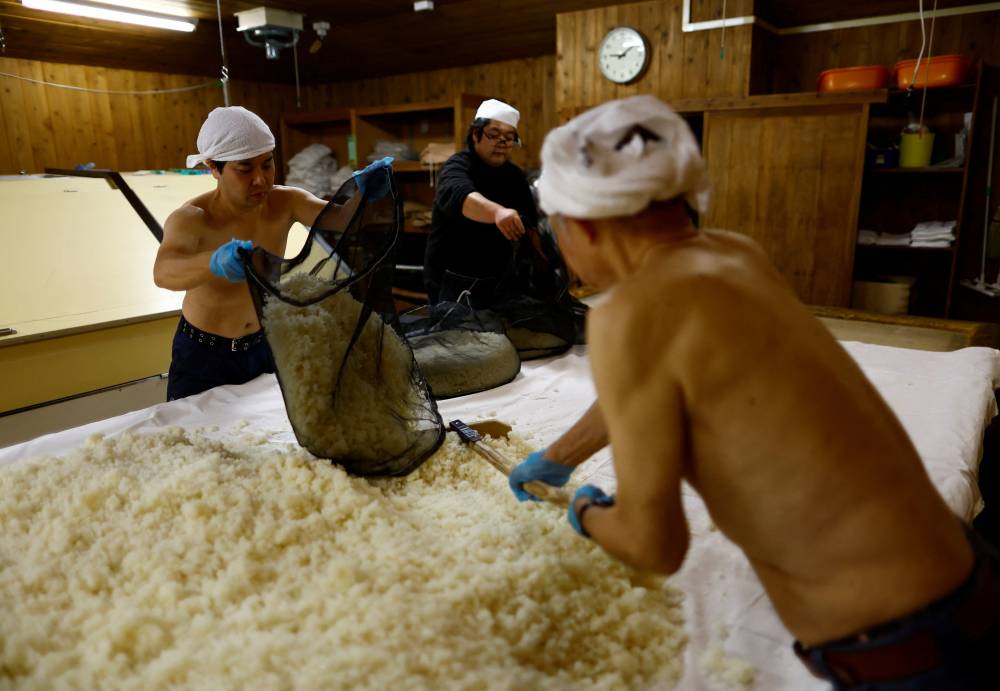
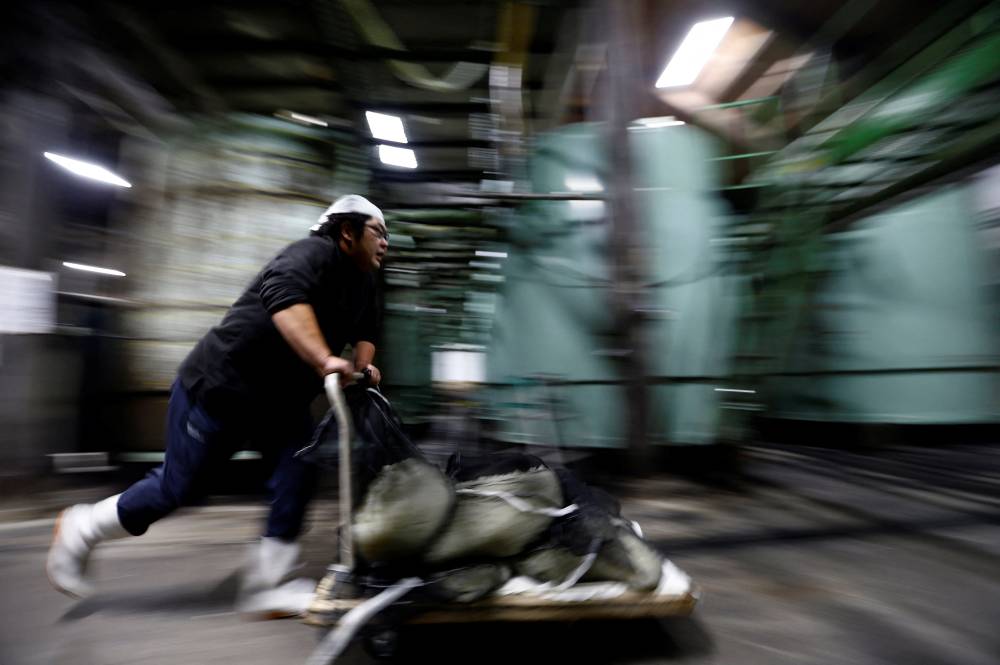
The centuries-old method of making sake is unique for its three-step preparation, or “San-Dan-Jikomi“, of allowing multiple fermentation processes to progress simultaneously in a single container.

“It’s really cool just seeing and understanding how it all comes together,” said Robert Brown, an American visitor at the brewery. “Taking a lot of Japan’s history and then turning it into a cultural heritage seems really cool to me.”
While sake has lost ground as a regular drink, Maesako said it remains impossible to separate from Japanese culture.

“We have sake at celebrations, at New Year’s, and also on sad occasions, like funerals,” he said. “The culture of Japanese sake is the culture of Japan itself.”
The brewing technique is expected to be formally endorsed at a Unesco committee session in Paraguay this week. It will be Japan’s 23rd entry on the list of Intangible Cultural Heritage.
Reuters, the news and media division of Thomson Reuters, is the world’s largest multimedia news provider, reaching billions of people worldwide every day. Reuters provides business, financial, national and international news to professionals via desktop terminals, the world's media organizations, industry events and directly to consumers.